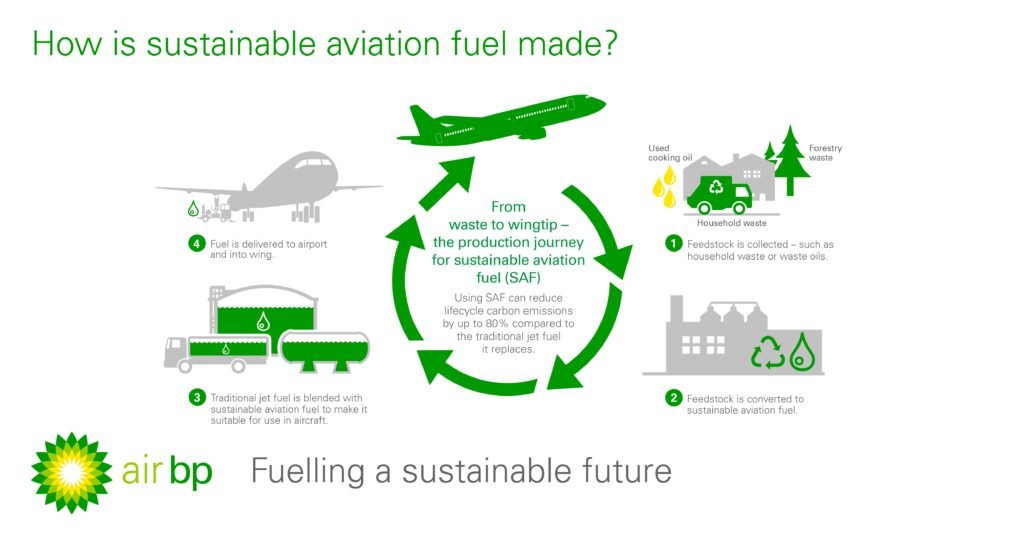
Sustainable Aviation Fuel
Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is an alternative fuel made from non-petroleum feedstocks that reduces emissions from air transportation. SAF can be blended at different levels with limits between 10% and 50%, depending on the feedstock and how the fuel is produced. According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), over 360,000 commercial flights have used SAF at 46 different airports largely concentrated in the United States and Europe.
Worldwide, aviation accounts for 2% of all carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and 12% of all CO2 emissions from transportation. ICAO’s Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) caps net CO2 aviation emissions at 2020 levels through 2035. The international aviation industry has set an aspirational goal to reach net zero carbon by 2050. SAF presents the best near-term opportunity to meet these goals. The Sustainable Aviation Fuel Grand Challenge, announced in 2021, brings together multiple federal agencies for the purpose of expanding domestic consumption to 3 billion gallons in 2030 and 35 billion gallons in 2050 while achieving at least a 50% reduction in lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits
Renewable hydrocarbon biocarbon fuels offer many benefits, including:
- Engine and infrastructure compatibility—SAF blended with conventional Jet A can be used in existing aircraft and infrastructure.
- Fewer emissions—Compared with conventional jet fuel, 100% SAF has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 94% depending on feedstock and technology pathway.
- More flexibility—SAF is a replacement for conventional jet fuel, allowing for multiple products from various feedstocks and production technologies.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding the Need for Sustainable Aviation Fuel
- Importance of Sustainable Practices in Aviation
- What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel?
- Defining Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
- Differentiating SAF from Conventional Jet Fuel
- Production Methods
- Biomass Conversion Processes
- Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids (HEFA)
- Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis
- Power-to-Liquid (PtL) Technologies
- Environmental Benefits
- Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction
- Air Quality Improvement
- Potential for Carbon Neutrality
- Economic and Social Impacts
- Economic Viability of SAF Production
- Job Creation and Industry Growth
- Community and Stakeholder Engagement
- Challenges and Limitations
- Feedstock Availability and Sustainability
- Infrastructure Development
- Policy and Regulatory Hurdles
- Current Initiatives and Adoption
- Global Efforts to Promote SAF
- Case Studies of Successful Implementations
- Future Outlook
- Forecasting the Role of SAF in Aviation
- Technological Advancements and Innovation
- Conclusion
- Recapitulation of SAF’s Potential
- Call to Action for Industry Stakeholders
- References
What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel?
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is an alternative to traditional fossil-based aviation fuels, derived from renewable resources such as plant biomass, agricultural residues, waste oils, and other sustainable feedstocks. Unlike conventional jet fuels, SAF offers a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions throughout its lifecycle, making it a vital component in the aviation industry’s efforts to achieve sustainability goals.
Production Methods
Several production methods are utilized to manufacture Sustainable Aviation Fuel, including biomass conversion processes, hydroprocessing, Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, and power-to-liquid technologies. Each method has its advantages and challenges, contributing to the diverse landscape of SAF production.
Environmental Benefits
SAF presents a range of environmental benefits, including a substantial reduction in carbon dioxide emissions compared to conventional jet fuels. Additionally, SAF production can contribute to improved air quality and has the potential to achieve carbon neutrality when coupled with sustainable practices.
Economic and Social Impacts
The adoption of Sustainable Aviation Fuel not only benefits the environment but also has significant economic and social impacts. It creates opportunities for job creation, fosters industry growth, and enhances community engagement, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient aviation sector.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, SAF faces several challenges and limitations, including feedstock availability, infrastructure requirements, and regulatory barriers. Addressing these challenges is crucial to unlocking the full potential of Sustainable Aviation Fuel.
Current Initiatives and Adoption
Various initiatives and programs worldwide are promoting the adoption of SAF, with several airlines and airports already incorporating it into their operations. Case studies highlight successful implementations and provide valuable insights into the practical aspects of integrating SAF into aviation systems.
Future Outlook
The future of Sustainable Aviation Fuel looks promising, with ongoing research, technological advancements, and increasing awareness driving its adoption. As the aviation industry strives towards sustainability, SAF is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of air transportation.
Conclusion
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) represents more than just an alternative to conventional jet fuels; it symbolizes a commitment to environmental stewardship and a vision for a more sustainable aviation industry. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and strive to reduce our carbon footprint, SAF emerges as a beacon of hope, offering a tangible solution to mitigate the environmental impact of air travel.
The journey towards widespread adoption of SAF is not without its hurdles. It requires collaborative efforts from governments, industry leaders, researchers, and consumers to overcome challenges related to feedstock availability, infrastructure development, and policy frameworks. However, the benefits far outweigh the challenges.
By embracing Sustainable Aviation Fuel, we can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and enhance the overall sustainability of the aviation sector. Furthermore, SAF presents opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation, fostering a more resilient and prosperous industry.
As we look to the future, the continued support and investment in SAF are paramount. Research and development efforts must be intensified to refine production processes, expand feedstock options, and drive down costs. Moreover, policies and regulations should incentivize the adoption of SAF and create a conducive environment for its widespread use.
Ultimately, the transition to Sustainable Aviation Fuel is not just a choice but a necessity. It is a testament to our collective responsibility to safeguard the planet for future generations. By harnessing the potential of SAF, we can chart a course towards greener skies, where air travel is not just efficient and convenient but also environmentally sustainable. Together, let us embark on this journey towards a more sustainable aviation future.
References
https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/sustainable_aviation_fuel.html
https://www.iata.org/en/programs/environment/sustainable-aviation-fuels/